After we fix the communication model, synchrony, asynchrony, or partial synchrony, and a threshold adversary there are still five important modeling decisions regarding the adversary’s power:
- The type of corruption (passive, crash, omission, or Byzantine).
- The computational power of the adversary (unbounded, computational, or fine-grained).
- The adaptivity of the adversary (static, delayed adaptive, weak adaptive, adaptive, or strongly adaptive).
- The visibility of the adversary (full information or private channel).
- The mobility of the adversary (fixed or mobile).
1. Type of corruption
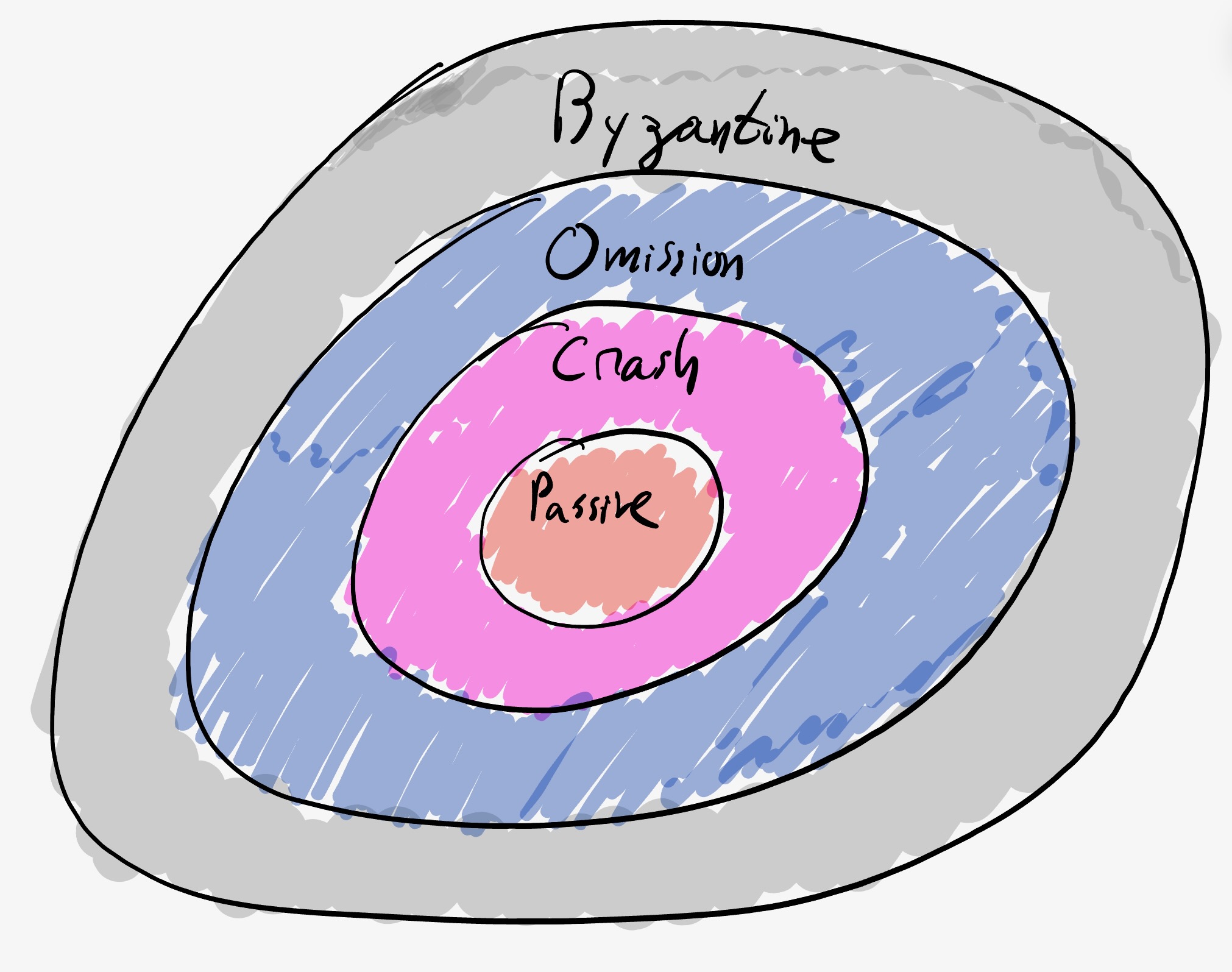
The first fundamental aspect is what type of corruption the adversary can inflict on the $f$ parties it can corrupt. There are four classic types of corruption: Passive, Crash, Omission, and Byzantine.
- Passive: a passively corrupted party must follow the protocol just like an honest party, but it allows the adversary to learn information. A passive adversary (sometimes called Honest-But-Curious or Semi-Honest) does not deviate from the protocol but can learn all possible information from its view: i.e., the messages sent and received by parties it controls. The adversary can aggregate all the views of the corrupted parties. Typically, the goal of the adversary designer is to limit the information that the adversary learns.
- Crash: in addition to passive, once the party is corrupted, the adversary can decide to cause a crash event which causes the party to stop sending and receiving all messages. The crash may occur mid-message, and once it happens, it is irrevocable.
- Omission: in addition to passive, once corrupted, the adversary can decide, for each message sent or each message received, to either drop or allow it to continue. The party is unaware of its corruption.
- Byzantine: this gives the adversary full power to control the party and take any (arbitrary) action on the corrupted party. This is also called active or arbitrary corruption.
Note that each corruption type subsumes the previous one.
There are other types of corruption. Most notable are variants of Covert adversaries. Covert adversaries can be used to model rational behavior where there is fear (utility loss) from punishment through some form of detection.
There are sub-variants of omission corruption:
- Send omission and Receive omission: which are in between crash and omission. See this post.
There is a subtle modeling choice for crash corruptions when a party sends messages to multiple parties in the same round:
- In the traditional model, prescribed order model, the protocol is allowed to prescribe the order of the messages, so the adversary can choose any prefix of this prescribed order to be sent before crashing. This requires the protocol to explicitly mention the order.
- In the more challenging model, adversarial order model, the protocol sends to a set of parties and the adversary can choose any sub-set of these messages to be sent before crashing.
These two models have a fundamental round complexity difference in early stopping, and seem to require another round for SMR.
2. Computational power
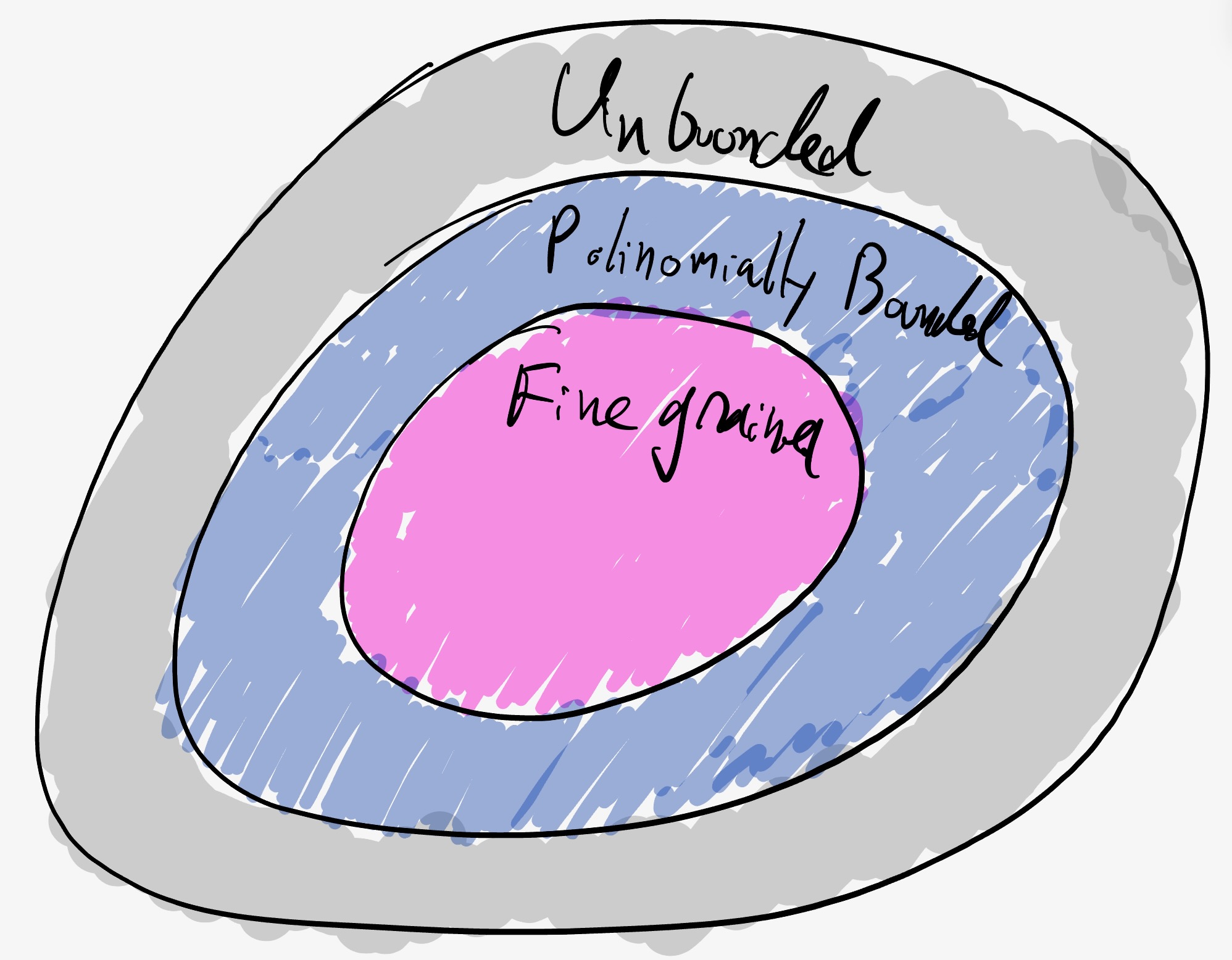
The computational power of the adversary:
-
Unbounded: the adversary has unbounded computational power. This model often leads to notions of perfect security or statistical security. The advantage of this model is that it remains secure indefinitely.
- Computationally bounded: the adversary has a polynomial advantage in computational power over the honest parties. Typically, this means that the adversary cannot (except with negligible probability) break the cryptographic primitives being used. For example, we typically assume the adversary cannot forge signatures of parties outside its control (see Goldreich’s chapter one for traditional CS formal definitions of polynomially bounded adversaries). All of modern cryptography depends on this type of adversary and typically there is a security parameter that needs to be updated over time (as computation becomes cheaper).
- Fine-grained computationally bounded: there is some concrete measure of computational power and the adversary is limited concretely. This model is used in proof-of-work based protocols. For example, see Andrychowicz and Dziembowski for a way to model the hash rate. It is often needed for Verifiable Delay Functions and time lock puzzles.
3. Adaptivity
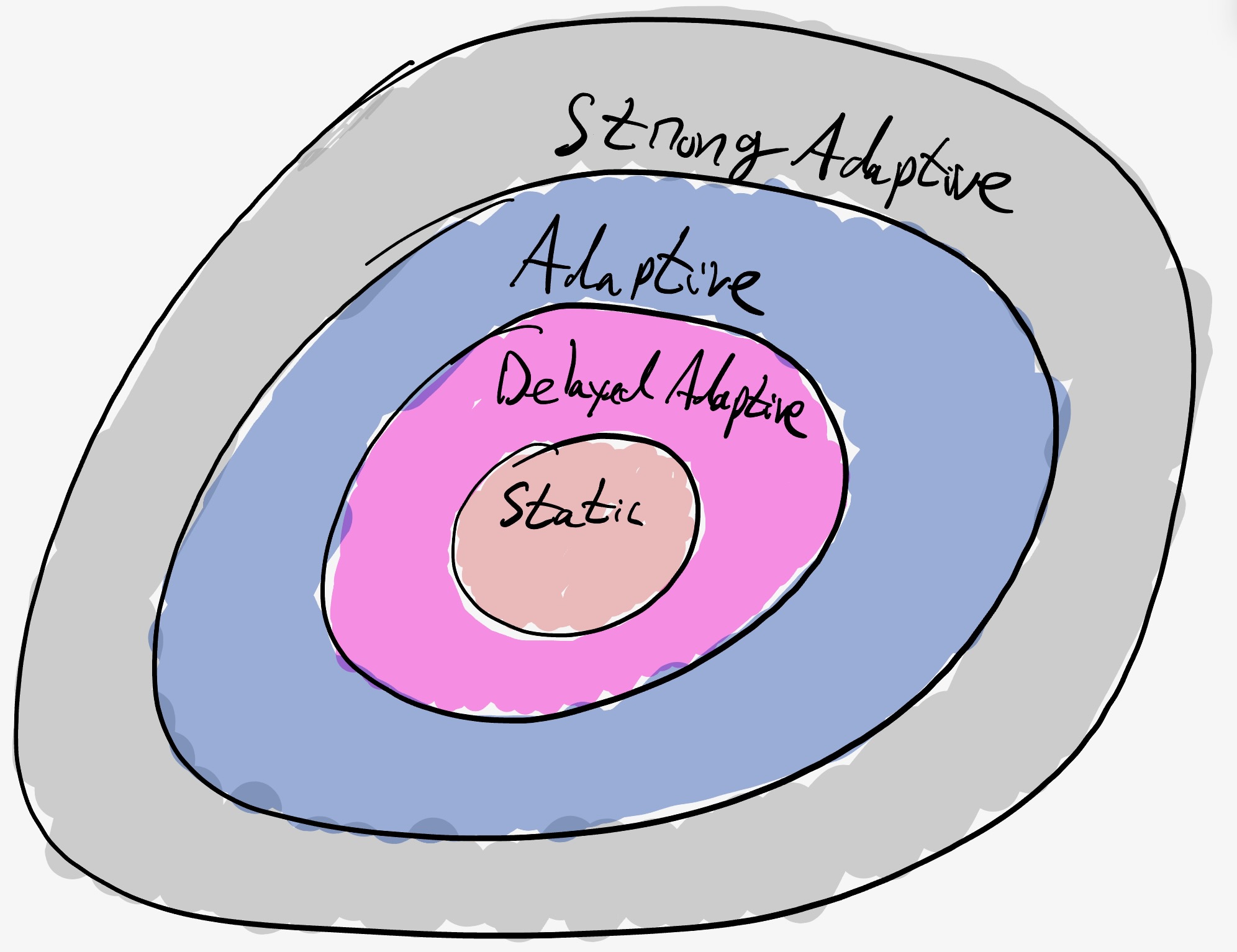
Adaptivity is the ability of the adversary to corrupt dynamically based on information the adversary learns during the execution.
-
Static: the adversary has to decide which $f$ parties to corrupt in advance before the execution of the protocol. Note that this is always sufficient when the protocol is deterministic because there are no surprises for the adversary. One natural thing for randomized protocols in this setting it to operate on a random subcommittee. This often leads to $O(n)$ message complexity.
-
Delayed Adaptive: given a parameter $k$, once the adversary asks to corrupt a party, the party is corrupted after $k \Delta$ time (or some notion of $k$ rounds in asynchrony). Leader based protocols in synchrony and partial synchrony can often obtain $O(1)$ expected time in this paradigm (using a weak randomness beacon). Linear-per-view protocols can obtain $O(n)$ expected messages after GST in this model.
-
Weak Adaptive: once the adversary asks to corrupt a party, the party is corrupted after it completes sending all its outgoing messages. Said differently, the corruption starts once the party looks at its incoming messages. So while the adversary is adaptive, the actual corruption may be delayed to after the party sends all its messages in that round (or in asynchrony after it sends all the messages it wants to immediately send). Sometimes in this model, it is also required that honest parties can safely erase some information in order to get forward security, or assume that messages always maintain FIFO order in each channel. This is the model used by Algorand and YOSO type protocols in synchrony.
-
Adaptive: once the adversary asks to corrupt a party, the party is immediately corrupted. Messages sent from the party before corruption cannot be erased (so will eventually arrive in asynchrony or arrive within $\Delta$ time in synchrony).
-
Strong Adaptive: once the adversary asks to corrupt a party, the party is immediately corrupted. Moreover, messages sent from the party before corruption that have not yet arrived can be erased (or clawed back) by the adversary. Some lower bounds assume this model to obtain a constant error. This model is sometimes called adaptive with claw back.
4. Visibility
The visibility is the power of the adversary to see the messages and the states of corrupted and non-corrupted parties.
-
Full information: the adversary sees the internal state of all parties and the content of all message sent. This often severely limits the protocol designer. See for example: Feige’s selection protocols, or Ben-Or et al’s Byzantine agreement. Often, the only thing that the adversary cannot do is predict the value of coins that have not been tossed yet.
-
Private channels: in this model, we assume the adversary cannot see the internal state of honest parties and cannot see the internal content of messages between honest parties. Each time a message between two honest parties is sent, the adversary learns the source, target, and message size. Depending on the communication model, it can decide to delay it by any value that is allowed by the communication model. The adversary can see the full internal state of corrupted parties.
-
Oblivious: the adversary can see the header of each message (source, destination, and message length) sent to and from a corrupt party, and based on that can decide its actions (crash, omit, delay, modify) depending on the adversary corruption type and network model. This type of adversary can model an adversary that has peripheral control (via a corrupt NIC, or local router/gateway). An oblivious omission adversary is often used to model an adversary that can maliciously corrupt parties that have a Trusted Execution Environments (TEEs) that cannot be corrupted.
-
Erasure model: in this model, once a party is corrupted, the adversary can see all the current state of the party, but cannot see data that was erased before the party was corrupted. This model is in contrast to a model where, once a party is corrupted, the adversary can see the full history of the party.
Rushing
For models that are round-based, another visibility distinction is the adversary’s ability to rush. When does the adversary see the messages sent to parties it controls? In the rushing adversary model, the adversary is allowed to see all the messages sent to parties it controls in round $i$ before it needs to decide what messages to send in its round $i$ messages. In the non-rushing adversary model, the adversary must commit to the round $i$ messages it sends before it receives any round $i$ messages from non-faulty parties.
5. Mobility
In the traditional fixed model the adversary is allowed to corrupt honest parties with some fixed budget of up to $f$ parties, but is not allowed to un-corrupt (or heal) corrupt parties back to being honest. In the mobile model the adversary is allowed to dynamically decide to corrupt and un-corrupt parties. The total number of corrupted parties at any given time is at most $f$, but over time the set of corrupted parties may change. It is often required that there is a gap between the time the adversary un-corrupts one party and the time it is allowed to corrupt another. This model was introduced by Ostrovsky and Yung and exemplified by proactive secret sharing. Another modeling decision is whether the party is aware that it is un-corrupted (in which case it may be able to remove in-memory corrupt data).
More models
There are many more models and variations - here is an incomplete list (let us know in the comments about more).
Mixed corruptions
In some cases, we are interested in a mix of say $f$ Byzantine and $k$ crash corruptions (for example here) or any other mix. For example, when the requirement is $n>3f+2k$ it can be thought of as if the adversary has a corruption budget of $n-1$ where each Byzantine corruption costs 3 and each crash corruption costs 2.
Sleepy model
In the sleepy model of Pass and Shi, in addition to being either honest or corrupt, parties may be active or inactive in each round. The assumption is that the threshold bound on the adversary holds at each round on the actual number of active parties in that round. This is sometimes called the dynamic participation model. This is similar to a model assuming a mix of Byzantine failures (with a corruption cost of 2) and mobile oblivious crash failures (with a corruption cost of 1).
Mobile sluggish
One of the challenges in the mobile model is the fact that the adversary can accumulate the private keys of parties. In the weak synchrony model (also called mobile sluggish), the adversary is allowed to corrupt either via a Byzantine corruption (that is not mobile) or a mobile sluggish corruption. Critically, the sluggish corruption allows the adversary to delay messages to and from the corrupted party but not to learn its private keys. Hence, allowing sluggish corruptions to be mobile does not allow the adversary to accumulate private keys. This is similar to assuming a mix of Byzantine failures and mobile oblivious omission failures.
Flexible model
The Flexible BFT model introduces two variations. First, a model where different properties hold under different threshold assumptions. Second, a model where the same protocol may serve different clients, where each client may have a different adversary threshold in mind.
Acknowledgments
Special thanks to Alin Tomescu, Kartik Nayak, Gilad Stern, and Tim Roughgarden for insightful comments.
Please leave comments on Twitter